My journey continues
👋 Hi, I’m Bjørnar Lintvedt
I’m a Senior Network Consultant at Bluetree, working at the intersection of networking and software development.
As mentioned in my first blog post, I’m preparing for the CCIE Automation lab exam — Cisco’s most advanced certification for network automation and programmability. I’m documenting the journey here with weekly, hands-on blog posts tied to the blueprint.
Link to my GitLab Repo
Blog post #7
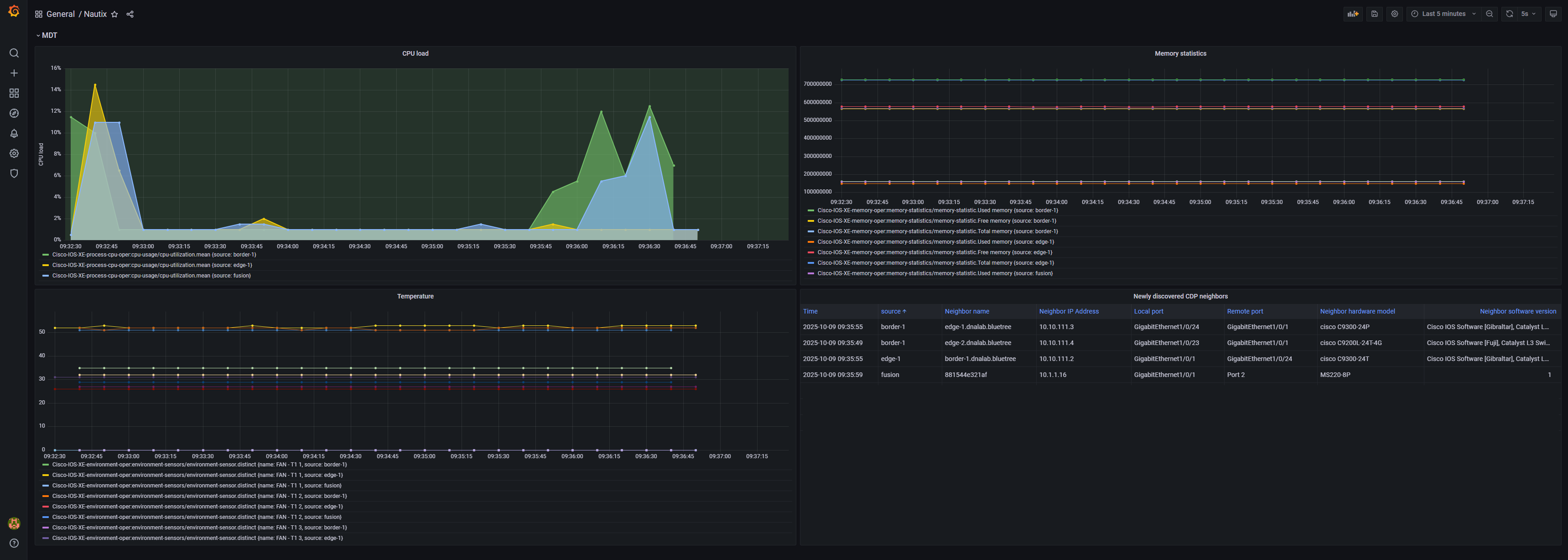
This week I wanted to dive deeper into Model-Driven Telemetry (MDT). Instead of manually polling devices for operational data, MDT allows streaming real-time metrics from network devices to monitoring systems — giving insights into performance, state, and anomalies as they happen.
Why Model-Driven Telemetry?
Model-Driven Telemetry is the foundation for proactive, data-driven network operations. It lets us:
-
Stream metrics from devices in real-time (CPU, memory, interfaces, BGP peers)
-
Use YANG models to define exactly what data we want
-
Choose between periodic polling, periodic push, or event-driven subscriptions
-
Visualize data in Grafana or feed it into analytics platforms
This Week’s Project
I created a MDT solution for Cisco IOS-XE devices, integrated into my Nautix platform:
-
Subscriptions: Created using YANG models to collect CPU, memory, temperature and CDP neighbors operational data
-
Streaming: Configured dial-out gRPC telemetry to Telegraf
-
Visualization: Built Grafana dashboard showing device metrics
-
Optimization: Tuned subscriptions with XPath filters, cadence settings, and on-change triggers
Getting Started
Before configuring telemetry on your devices, you need the TIG stack (Telegraf → InfluxDB → Grafana) to receive and visualize the data. Here’s how I set it up locally using Docker Compose.
1. Start the TIG stack
I assume you have already cloned the repository and have done the initial setup as per readme.
In the root of the repositoryrepo, do:
docker-compose up
This spins up:
-
InfluxDB – stores telemetry data
-
Grafana – dashboards and visualization
-
Telegraf – optional local agent if needed for transformation or collection
- Other Nautix services
2. Run the Ansible Playbook
Configure telemetry subscriptions on your devices (ensure you have run device discovery first):
This playbook:
-
Creates subscriptions using YANG models
-
Configures cadence, on-change triggers, and dial-out streams
-
Points the telemetry data to your InfluxDB instance
3. Check the Telemetry Stream
On the devices, verify subscriptions:
Check that the subscription is connected to Telegraf:
4. Visualize in Grafana
- Open Grafana (
http://localhost:3000), login with admin/secret
- Add an InfluxDB data source pointing to your InfluxDB container
- Import dashboard:
services/grafana/nautix_dashboard.json
- Explore real-time device metrics in the dashboard
Implementation
Here’s the updated folder structure reflecting new or modified files:
📂 services/automation/ansible/
📂 services/grafana/
📂 services/telegraf/
📂 docker-compose.yml – Spins up InfluxDB, Grafana, Telegraf, and rest of the Nautix app
Let’s break it down step by step.
1. Ansible Playbooks
2. TIG Stack
3. Telegraf configuration
4. Influx DB configuration
-
Set up very basic
Why This Matters
Before, operational data required manual CLI commands or SNMP polling. Now:
✔ Metrics are streamed continuously, reducing lag
✔ On-change subscriptions minimize unnecessary data
✔ Dashboards provide actionable insights at a glance
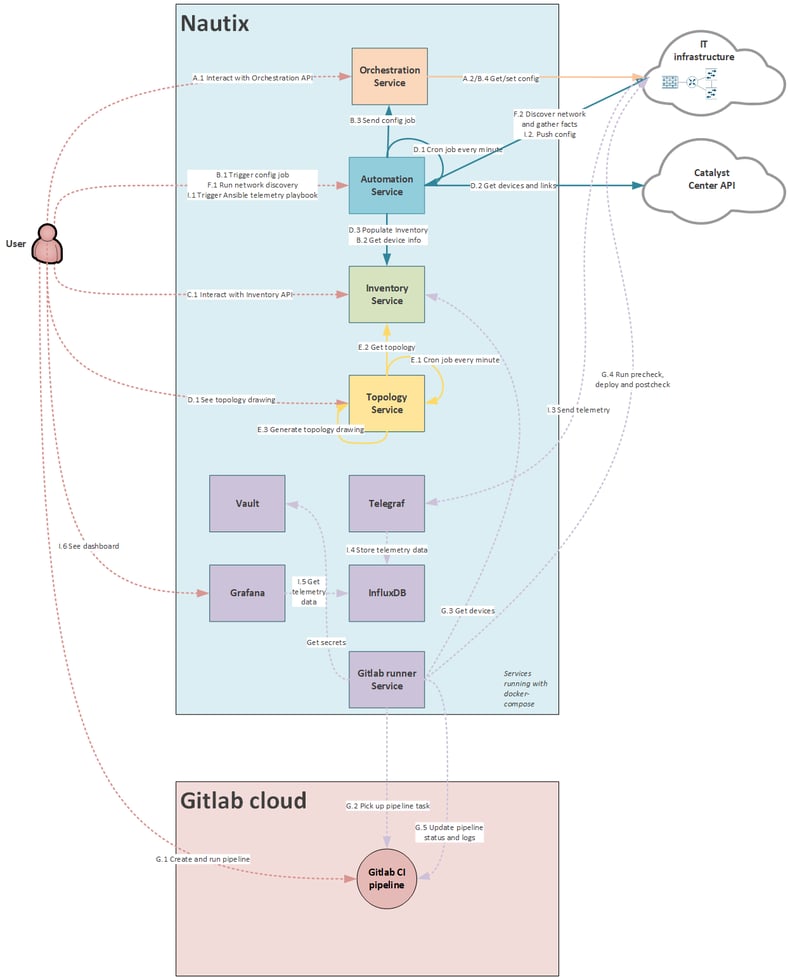
Nautix architecture
Use case "I": Model driven telemetry
- I.1 Trigger ansible playbook to configure telemetry subscription on Cisco IOS XE devices
- I.2 Ansible runs playbook
- I.3 Network devices starts sending telemetry data to Telegraf
- I.4 Telegraf stores the telemetry data to InfluxDB
- I.5 User shows dashboard
- I.6 Grafana polls telemetry data from InfluxDB
- User seeing the telemetry data :)
📅 What’s Next
Post #8 I have not decided yet. It will be a surprise :)
🔗 Useful Links
Blog series